Issue published July 1, 2016 Previous issue | Next issue

- Volume 126, Issue 7
Go to section:
On the cover: Mitochondrial metabolism in asthma
-
Op-Eds
Andrew R. MarksAndrew R. MarksPublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2385-2387. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88434.×Abstract
The 5th anniversary of the Fukushima disaster and the 30th anniversary of the Chernobyl disaster, the two most catastrophic nuclear accidents in history, both occurred recently. Images of Chernobyl are replete with the international sign of radioactive contamination (a circle with three broad spokes radiating outward in a yellow sign). In contrast, ongoing decontamination efforts at Fukushima lack international warnings about radioactivity. Decontamination workers at Fukushima appear to be poorly protected against radiation. It is almost as if the effort is to make the Fukushima problem disappear. A more useful response would be to openly acknowledge the monumental problems inherent in managing a nuclear plant disaster. Lessons from Chernobyl are the best predictors of what the Fukushima region of Japan is coping with in terms of health and environmental problems following a nuclear catastrophe.
Authors
Andrew R. Marks
David G. Nathan, David M. NathanDavid G. Nathan, David M. NathanPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2388-2391. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88381.×Abstract
The extramural General Clinical Research Center (GCRC) program has been funded for more than 50 years, first by the National Center for Research Resources, NIH, and more recently as part of the Clinical Translational Science Award (CTSA) program through the newly formed National Center for Advancing Translation Sciences (NCATS). The GCRCs represent the federally funded laboratories that employ a highly trained cadre of research nurses, dietitians, and other support staff and in which generations of clinical investigators trained and performed groundbreaking human studies that advanced medical science and improved clinical care. Without the opportunity for adequate discussion, NCATS has now stopped funding these Research Centers. In this “eulogy,” we review the origins and history of the GCRCs, their contributions to the advancement of medicine, and the recent events that have essentially defunded them. We mourn their loss.
Authors
David G. Nathan, David M. Nathan
-
Conversations with Giants in Medicine
Ushma S. NeillUshma S. NeillPublished July 1, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2392-2393. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88964.
-
Reviews
Anuradha Ray, … , Prabir Ray, Sally E. WenzelAnuradha Ray, … , Prabir Ray, Sally E. WenzelPublished July 1, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2394-2403. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI84144.×Abstract
The term asthma encompasses a disease spectrum with mild to very severe disease phenotypes whose traditional common characteristic is reversible airflow limitation. Unlike milder disease, severe asthma is poorly controlled by the current standard of care. Ongoing studies using advanced molecular and immunological tools along with improved clinical classification show that severe asthma does not identify a specific patient phenotype, but rather includes patients with constant medical needs, whose pathobiologic and clinical characteristics vary widely. Accordingly, in recent clinical trials, therapies guided by specific patient characteristics have had better outcomes than previous therapies directed to any subject with a diagnosis of severe asthma. However, there are still significant gaps in our understanding of the full scope of this disease that hinder the development of effective treatments for all severe asthmatics. In this Review, we discuss our current state of knowledge regarding severe asthma, highlighting different molecular and immunological pathways that can be targeted for future therapeutic development.
Authors
Anuradha Ray, Mahesh Raundhal, Timothy B. Oriss, Prabir Ray, Sally E. Wenzel
Leticia Corrales, … , Thomas W. Dubensky Jr., Thomas F. GajewskiLeticia Corrales, … , Thomas W. Dubensky Jr., Thomas F. GajewskiPublished July 1, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2404-2411. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86892.×Abstract
A major subset of human cancers shows evidence for spontaneous adaptive immunity, which is reflected by the presence of infiltrating CD8+ T cells specific for tumor antigens within the tumor microenvironment. This observation has raised the question of which innate immune sensing pathway might detect the presence of cancer and lead to a natural adaptive antitumor immune response in the absence of exogenous infectious pathogens. Evidence for a critical functional role for type I IFNs led to interrogation of candidate innate immune sensing pathways that might be triggered by tumor presence and induce type I IFN production. Such analyses have revealed a major role for the stimulator of IFN genes pathway (STING pathway), which senses cytosolic tumor–derived DNA within the cytosol of tumor-infiltrating DCs. Activation of this pathway is correlated with IFN-β production and induction of antitumor T cells. Based on the biology of this natural immune response, pharmacologic agonists of the STING pathway are being developed to augment and optimize STING activation as a cancer therapy. Intratumoral administration of STING agonists results in remarkable therapeutic activity in mouse models, and STING agonists are being carried forward into phase I clinical testing.
Authors
Leticia Corrales, Sarah M. McWhirter, Thomas W. Dubensky Jr., Thomas F. Gajewski
-
Commentaries
Stephen G. KalerStephen G. KalerPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2412-2414. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88617.×Abstract
The severe liver pathology of untreated Wilson disease (WD) is associated with massive copper overload caused by mutations in a liver-specific copper-transporting ATPase, ATP7B. While early, presymptomatic detection and chelation with conventional copper-binding molecules enables effective and life-saving treatment, liver transplantation is the sole option currently available for those with advanced disease. In this issue of the
JCI , Lichtmannegger, Leitzinger, and colleagues delineate the therapeutic effect of methanobactin (MB), a potent bacterial copper-binding protein, at three late stages of disease in a WD rat model. Their results suggest that a formal clinical trial of MB in human subjects with severe hepatic pathology caused by WD would be rational.Authors
Stephen G. Kaler
×Abstract
Targeting glioblastoma stem cells with γ-secretase inhibitors (GSIs) disrupts the Notch pathway and has shown some benefit in both pre-clinical models and in patients during phase I/II clinical trials. However, it is largely unknown why some glioblastoma (GBM) does not respond to GSI treatment. In this issue of the
JCI , Xie et al. determined that GSI-resistant brain tumor–initiating cells (BTICs) from GBM express a higher level of the geneRBPJ , which encodes a mediator of canonical Notch signaling, compared to non-BTICs. Knockdown of RBPJ in BTICs decreased propagation in vitro and in vivo by inducing apoptosis. Interestingly, RBPJ was shown to regulate a different transcription program than Notch in BTICs by binding CDK9, thereby affecting Pol II–regulated transcript elongation. Targeting CDK9 or c-MYC, an upstream regulator of RBPJ, with small molecules also decreased BTIC propagation, and prolonged survival in mice bearing orthotopic GBM xenografts. This study not only provides a mechanism for GSI treatment resistance, but also identifies two potential therapeutic strategies to target GSI-resistant BTICs.Authors
Xing Fan
Dheeraj Bhavanasi, … , Kelsey F. Speer, Peter S. KleinDheeraj Bhavanasi, … , Kelsey F. Speer, Peter S. KleinPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2419-2421. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88620.×Abstract
The secretory protein Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) is a known Wnt antagonist and has been shown to suppress tumorigenesis in some cancer cells; however, it is also upregulated in many types of cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Wnt-independent mechanisms by which DKK-1 promotes cancer cell proliferation are not well understood. In this issue of the
JCI , Kimura and colleagues demonstrate that DKK-1 interacts with cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) to promote activation of AKT. They show that both DKK-1 and CKAP4 are frequently upregulated in pancreatic and lung cancers. Importantly, targeting this interaction with an anti-CKAP4 antibody prevented tumor formation in murine xenograft models. These results identify a previously unrecognized DKK-1–mediated pathway and suggest CKAP4 as a potential therapeutic target for certain cancers.Authors
Dheeraj Bhavanasi, Kelsey F. Speer, Peter S. Klein
Mandy L. FordMandy L. FordPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2422-2424. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88621.×Abstract
Increasing evidence indicates that microbes have a large influence on immune function. Previous studies have linked pathogenic microorganisms with decreased allograft tolerance and subsequent rejection. In this issue of the
JCI , Lei and colleagues demonstrate that commensal organisms also influence the host response to allograft transplantation. Using murine skin and cardiac transplant models, the authors demonstrate that allograft rejection is accelerated in mice with a normal microbiome compared with germ-free animals and antibiotic-treated mice. The increased graft rejection observed in conventional animals was due to enhanced T cell priming and was mediated through type I IFN. Together, these results suggest that altering a patient’s microbial community prior to transplant could improve allograft acceptance.Authors
Mandy L. Ford
-
Research Articles
Anna Waldhuber, … , Catharina Svanborg, Thomas MiethkeAnna Waldhuber, … , Catharina Svanborg, Thomas MiethkePublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2425-2436. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81916.×Abstract
Successful bacterial pathogens produce an array of virulence factors that allow subversion of the immune system and persistence within the host. For example, uropathogenic
Escherichia coli strains, such as CFT073, express Toll/IL-1 receptor–containing (TIR-containing) protein C (TcpC), which impairs TLR signaling, thereby suppressing innate immunity in the urinary tract and enhancing persistence in the kidneys. Here, we have reported that TcpC also reduces secretion of IL-1β by directly interacting with the NACHT leucin-rich repeat PYD protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome, which is crucial for recognition of pathogens within the cytosol. At a low MOI, IL-1β secretion was minimal in CFT073-infected macrophages; however, IL-1β release was markedly increased in macrophages infected with CFT073 lackingtcpC . Induction of IL-1β secretion by CFT073 andtcpC –deficient CFT073 required the NLRP3 inflammasome. TcpC attenuated activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by binding both NLRP3 and caspase-1 and thereby preventing processing and activation of caspase-1. Moreover, in a murine urinary tract infection model, CFT073 infection rapidly induced expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the bladder mucosa; however, the presence of TcpC in WT CFT073 reduced IL-1β levels in the urine of infected mice. Together, these findings illustrate how uropathogenicE .coli use the multifunctional virulence factor TcpC to attenuate innate immune responses in the urinary tract.Authors
Anna Waldhuber, Manoj Puthia, Andreas Wieser, Christine Cirl, Susanne Dürr, Silke Neumann-Pfeifer, Simone Albrecht, Franziska Römmler, Tina Müller, Yunji Zheng, Sören Schubert, Olaf Groß, Catharina Svanborg, Thomas Miethke
Anees Fatima, … , Yoh-suke Mukouyama, Tsutomu KumeAnees Fatima, … , Yoh-suke Mukouyama, Tsutomu KumePublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2437-2451. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI80465.×Abstract
The lymphatic vasculature is essential for maintaining interstitial fluid homeostasis, and dysfunctional lymphangiogenesis contributes to various pathological processes, including inflammatory disease and tumor metastasis. Mutations in
FOXC2 are dominantly associated with late-onset lymphedema; however, the precise role of FOXC2 and a closely related factor, FOXC1, in the lymphatic system remains largely unknown. Here we identified a molecular cascade by which FOXC1 and FOXC2 regulate ERK signaling in lymphatic vessel growth. In mice, lymphatic endothelial cell–specific (LEC-specific) deletion ofFoxc1 ,Foxc2 , or both resulted in increased LEC proliferation, enlarged lymphatic vessels, and abnormal lymphatic vessel morphogenesis. Compared with LECs from control animals, LECs from mice lacking bothFoxc1 andFoxc2 exhibited aberrant expression of Ras regulators, and embryos with LEC-specific deletion ofFoxc1 andFoxc2 , alone or in combination, exhibited ERK hyperactivation. Pharmacological ERK inhibition in utero abolished the abnormally enlarged lymphatic vessels in FOXC-deficient embryos. Together, these results identify FOXC1 and FOXC2 as essential regulators of lymphangiogenesis and indicate a new potential mechanistic basis for lymphatic-associated diseases.Authors
Anees Fatima, Ying Wang, Yutaka Uchida, Pieter Norden, Ting Liu, Austin Culver, William H. Dietz, Ford Culver, Meredith Millay, Yoh-suke Mukouyama, Tsutomu Kume
Elisa Lenti, … , Paul A. Trainor, Andrea BrendolanElisa Lenti, … , Paul A. Trainor, Andrea BrendolanPublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2452-2464. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI82956.×Abstract
The molecular mechanisms that underlie spleen development and congenital asplenia, a condition linked to increased risk of overwhelming infections, remain largely unknown. The transcription factor TLX1 controls cell fate specification and organ expansion during spleen development, and
Tlx1 deletion causes asplenia in mice. Deregulation ofTLX1 expression has recently been proposed in the pathogenesis of congenital asplenia in patients carrying mutations of the gene-encoding transcription factor SF-1. Herein, we have shown that TLX1-dependent regulation of retinoic acid (RA) metabolism is critical for spleen organogenesis. In a murine model, loss ofTlx1 during formation of the splenic anlage increased RA signaling by regulating several genes involved in RA metabolism. Uncontrolled RA activity resulted in premature differentiation of mesenchymal cells and reduced vasculogenesis of the splenic primordium. Pharmacological inhibition of RA signaling inTlx1 -deficient animals partially rescued the spleen defect. Finally, spleen growth was impaired in mice lacking either cytochrome P450 26B1 (Cyp26b1 ), which results in excess RA, or retinol dehydrogenase 10 (Rdh10 ), which results in RA deficiency. Together, these findings establish TLX1 as a critical regulator of RA metabolism and provide mechanistic insights into the molecular determinants of human congenital asplenia.Authors
Elisa Lenti, Diego Farinello, Kazunari K. Yokoyama, Dmitry Penkov, Laura Castagnaro, Giovanni Lavorgna, Kenly Wuputra, Lisa L. Sandell, Naomi E. Butler Tjaden, Francesca Bernassola, Nicoletta Caridi, Anna De Antoni, Michael Wagner, Katja Kozinc, Karen Niederreither, Francesco Blasi, Diego Pasini, Gregor Majdic, Giovanni Tonon, Paul A. Trainor, Andrea Brendolan
Weiling Xu, … , Satish C. Kalhan, Serpil C. ErzurumWeiling Xu, … , Satish C. Kalhan, Serpil C. ErzurumPublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2465-2481. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI82925.×Abstract
High levels of arginine metabolizing enzymes, including inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and arginase (ARG), are typical in asthmatic airway epithelium; however, little is known about the metabolic effects of enhanced arginine flux in asthma. Here, we demonstrated that increased metabolism sustains arginine availability in asthmatic airway epithelium with consequences for bioenergetics and inflammation. Expression of iNOS, ARG2, arginine synthetic enzymes, and mitochondrial respiratory complexes III and IV was elevated in asthmatic lung samples compared with healthy controls. ARG2 overexpression in a human bronchial epithelial cell line accelerated oxidative bioenergetic pathways and suppressed hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) and phosphorylation of the signal transducer for atopic Th2 inflammation STAT6 (pSTAT6), both of which are implicated in asthma etiology.
Arg2 -deficient mice had lower mitochondrial membrane potential and greater HIF-2α than WT animals. In an allergen-induced asthma model, mice lackingArg2 had greater Th2 inflammation than WT mice, as indicated by higher levels of pSTAT6, IL-13, IL-17, eotaxin, and eosinophils and more mucus metaplasia. Bone marrow transplants fromArg2 -deficient mice did not affect airway inflammation in recipient mice, supporting resident lung cells as the drivers of elevated Th2 inflammation. These data demonstrate that arginine flux preserves cellular respiration and suppresses pathological signaling events that promote inflammation in asthma.Authors
Weiling Xu, Sudakshina Ghosh, Suzy A.A. Comhair, Kewal Asosingh, Allison J. Janocha, Deloris A. Mavrakis, Carole D. Bennett, Lourdes L. Gruca, Brian B. Graham, Kimberly A. Queisser, Christina C. Kao, Samuel H. Wedes, John M. Petrich, Rubin M. Tuder, Satish C. Kalhan, Serpil C. Erzurum
Eric S. Wohleb, … , Meenakshi Alreja, Ronald S. DumanEric S. Wohleb, … , Meenakshi Alreja, Ronald S. DumanPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2482-2494. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85033.×Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a recurring psychiatric illness that causes substantial health and socioeconomic burdens. Clinical reports have revealed that scopolamine, a nonselective muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, produces rapid antidepressant effects in individuals with MDD. Preclinical models suggest that these rapid antidepressant effects can be recapitulated with blockade of M1-type muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1-AChR); however, the cellular mechanisms underlying activity-dependent synaptic and behavioral responses to scopolamine have not been determined. Here, we demonstrate that the antidepressant-like effects of scopolamine are mediated by GABA interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Both GABAergic (GAD67+) interneurons and glutamatergic (CaMKII+) interneurons in the mPFC expressed M1-AChR. In mice, viral-mediated knockdown of M1-AChR specifically in GABAergic neurons, but not glutamatergic neurons, in the mPFC attenuated the antidepressant-like effects of scopolamine. Immunohistology and electrophysiology showed that somatostatin (SST) interneurons in the mPFC express M1-AChR at higher levels than parvalbumin interneurons. Moreover, knockdown of M1-AChR in SST interneurons in the mPFC demonstrated that M1-AChR expression in these neurons is required for the rapid antidepressant-like effects of scopolamine. These data indicate that SST interneurons in the mPFC are a promising pharmacological target for developing rapid-acting antidepressant therapies.
Authors
Eric S. Wohleb, Min Wu, Danielle M. Gerhard, Seth R. Taylor, Marina R. Picciotto, Meenakshi Alreja, Ronald S. Duman
Alexander M.K. Rothman, … , David J. Rowlands, Allan LawrieAlexander M.K. Rothman, … , David J. Rowlands, Allan LawriePublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2495-2508. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI83361.×Abstract
Loss of the growth-suppressive effects of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling has been demonstrated to promote pulmonary arterial endothelial cell dysfunction and induce pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation, leading to the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). MicroRNAs (miRs) mediate higher order regulation of cellular function through coordinated modulation of mRNA targets; however, miR expression is altered by disease development and drug therapy. Here, we examined treatment-naive patients and experimental models of PAH and identified a reduction in the levels of miR-140-5p. Inhibition of miR-140-5p promoted PASMC proliferation and migration in vitro. In rat models of PAH, nebulized delivery of miR-140-5p mimic prevented the development of PAH and attenuated the progression of established PAH. Network and pathway analysis identified SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (SMURF1) as a key miR-140-5p target and regulator of BMP signaling. Evaluation of human tissue revealed that SMURF1 is increased in patients with PAH. miR-140-5p mimic or SMURF1 knockdown in PASMCs altered BMP signaling, further supporting these factors as regulators of BMP signaling. Finally,
Smurf1 deletion protected mice from PAH, demonstrating a critical role in disease development. Together, these studies identify both miR-140-5p and SMURF1 as key regulators of disease pathology and as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of PAH.Authors
Alexander M.K. Rothman, Nadine D. Arnold, Josephine A. Pickworth, James Iremonger, Loredana Ciuclan, Robert M.H. Allen, Sabine Guth-Gundel, Mark Southwood, Nicholas W. Morrell, Matthew Thomas, Sheila E. Francis, David J. Rowlands, Allan Lawrie
Lei Pei, … , William J. Welch, Alan S.L. YuLei Pei, … , William J. Welch, Alan S.L. YuPublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2509-2518. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI83942.×Abstract
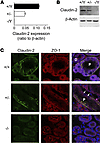
Efficient oxygen utilization in the kidney may be supported by paracellular epithelial transport, a form of passive diffusion that is driven by preexisting transepithelial electrochemical gradients. Claudins are tight-junction transmembrane proteins that act as paracellular ion channels in epithelial cells. In the proximal tubule (PT) of the kidney, claudin-2 mediates paracellular sodium reabsorption. Here, we used murine models to investigate the role of claudin-2 in maintaining energy efficiency in the kidney. We found that claudin-2–null mice conserve sodium to the same extent as WT mice, even during profound dietary sodium depletion, as a result of the upregulation of transcellular Na-K-2Cl transport activity in the thick ascending limb of Henle. We hypothesized that shifting sodium transport to transcellular pathways would lead to increased whole-kidney oxygen consumption. Indeed, compared with control animals, oxygen consumption in the kidneys of claudin-2–null mice was markedly increased, resulting in medullary hypoxia. Furthermore, tubular injury in kidneys subjected to bilateral renal ischemia-reperfusion injury was more severe in the absence of claudin-2. Our results indicate that paracellular transport in the PT is required for efficient utilization of oxygen in the service of sodium transport. We speculate that paracellular permeability may have evolved as a general strategy in epithelial tissues to maximize energy efficiency.
Authors
Lei Pei, Glenn Solis, Mien T.X. Nguyen, Nikhil Kamat, Lynn Magenheimer, Min Zhuo, Jiahua Li, Joshua Curry, Alicia A. McDonough, Timothy A. Fields, William J. Welch, Alan S.L. Yu
Nicola M. Tomas, … , Catherine Meyer-Schwesinger, Rolf A.K. StahlNicola M. Tomas, … , Catherine Meyer-Schwesinger, Rolf A.K. StahlPublished May 23, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2519-2532. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85265.×Abstract
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults, and one-third of patients develop end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Circulating autoantibodies against the podocyte surface antigens phospholipase A2 receptor 1 (PLA2R1) and the recently identified thrombospondin type 1 domain–containing 7A (THSD7A) are assumed to cause the disease in the majority of patients. The pathogenicity of these antibodies, however, has not been directly proven. Here, we have reported the analysis and characterization of a male patient with THSD7A-associated MN who progressed to ESRD and subsequently underwent renal transplantation. MN rapidly recurred after transplantation. Enhanced staining for THSD7A was observed in the kidney allograft, and detectable anti-THSD7A antibodies were present in the serum before and after transplantation, suggesting that these antibodies induced a recurrence of MN in the renal transplant. In contrast to PLA2R1, THSD7A was expressed on both human and murine podocytes, enabling the evaluation of whether anti-THSD7A antibodies cause MN in mice. We demonstrated that human anti-THSD7A antibodies specifically bind to murine THSD7A on podocyte foot processes, induce proteinuria, and initiate a histopathological pattern that is typical of MN. Furthermore, anti-THSD7A antibodies induced marked cytoskeletal rearrangement in primary murine glomerular epithelial cells as well as in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Our findings support a causative role of anti-THSD7A antibodies in the development of MN.
Authors
Nicola M. Tomas, Elion Hoxha, Anna T. Reinicke, Lars Fester, Udo Helmchen, Jens Gerth, Friederike Bachmann, Klemens Budde, Friedrich Koch-Nolte, Gunther Zahner, Gabriele Rune, Gerard Lambeau, Catherine Meyer-Schwesinger, Rolf A.K. Stahl
Bradley Miller, … , John D. Imig, Andrey SorokinBradley Miller, … , John D. Imig, Andrey SorokinPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2533-2546. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI75079.×Abstract
Renal preglomerular arterioles regulate vascular tone to ensure a large pressure gradient over short distances, a function that is extremely important for maintaining renal microcirculation. Regulation of renal microvascular tone is impaired in salt-sensitive (SS) hypertension–induced nephropathy, but the molecular mechanisms contributing to this impairment remain elusive. Here, we assessed the contribution of the SH2 adaptor protein p66Shc (encoded by Shc1) in regulating renal vascular tone and the development of renal vascular dysfunction associated with hypertension-induced nephropathy. We generated a panel of mutant rat strains in which specific modifications of Shc1 were introduced into the Dahl SS rats. In SS rats, overexpression of p66Shc was linked to increased renal damage. Conversely, deletion of p66Shc from these rats restored the myogenic responsiveness of renal preglomerular arterioles ex vivo and promoted cellular contraction in primary vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) that were isolated from renal vessels. In primary SMCs, p66Shc restricted the activation of transient receptor potential cation channels to attenuate cytosolic Ca2+ influx, implicating a mechanism by which overexpression of p66Shc impairs renal vascular reactivity. These results establish the adaptor protein p66Shc as a regulator of renal vascular tone and a driver of impaired renal vascular function in hypertension-induced nephropathy.
Authors
Bradley Miller, Oleg Palygin, Victoriya A. Rufanova, Andrew Chong, Jozef Lazar, Howard J. Jacob, David Mattson, Richard J. Roman, Jan M. Williams, Allen W. Cowley Jr., Aron M. Geurts, Alexander Staruschenko, John D. Imig, Andrey Sorokin
Mario A. Acuña, … , Pierre-Jean Corringer, Hanns Ulrich ZeilhoferMario A. Acuña, … , Pierre-Jean Corringer, Hanns Ulrich ZeilhoferPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2547-2560. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI83817.×Abstract
Diminished inhibitory neurotransmission in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord is thought to contribute to chronic pain. In inflammatory pain, reductions in synaptic inhibition occur partially through prostaglandin E2- (PGE2-) and PKA-dependent phosphorylation of a specific subtype of glycine receptors (GlyRs) that contain α3 subunits. Here, we demonstrated that 2,6-di-
tert -butylphenol (2,6-DTBP), a nonanesthetic propofol derivative, reverses inflammation-mediated disinhibition through a specific interaction with heteromeric αβGlyRs containing phosphorylated α3 subunits. We expressed mutant GlyRs in HEK293T cells, and electrophysiological analyses of these receptors showed that 2,6-DTBP interacted with a conserved phenylalanine residue in the membrane-associated stretch between transmembrane regions 3 and 4 of the GlyR α3 subunit. In native murine spinal cord tissue, 2,6-DTBP modulated synaptic, presumably αβ heteromeric, GlyRs only after priming with PGE2. This observation is consistent with results obtained from molecular modeling of the α-β subunit interface and suggests that in α3βGlyRs, the binding site is accessible to 2,6-DTBP only after PKA-dependent phosphorylation. In murine models of inflammatory pain, 2,6-DTBP reduced inflammatory hyperalgesia in an α3GlyR-dependent manner. Together, our data thus establish that selective potentiation of GlyR function is a promising strategy against chronic inflammatory pain and that, to our knowledge, 2,6-DTBP has a unique pharmacological profile that favors an interaction with GlyRs that have been primed by peripheral inflammation.Authors
Mario A. Acuña, Gonzalo E. Yévenes, William T. Ralvenius, Dietmar Benke, Alessandra Di Lio, Cesar O. Lara, Braulio Muñoz, Carlos F. Burgos, Gustavo Moraga-Cid, Pierre-Jean Corringer, Hanns Ulrich Zeilhofer
Suzanne D. Burke, … , Iris Z. Jaffe, S. Ananth KarumanchiSuzanne D. Burke, … , Iris Z. Jaffe, S. Ananth KarumanchiPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2561-2574. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI83918.×Abstract
Preeclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy in which patients develop profound sensitivity to vasopressors, such as angiotensin II, and is associated with substantial morbidity for the mother and fetus. Enhanced vasoconstrictor sensitivity and elevations in soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFLT1), a circulating antiangiogenic protein, precede clinical signs and symptoms of preeclampsia. Here, we report that overexpression of
sFlt1 in pregnant mice induced angiotensin II sensitivity and hypertension by impairing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation and promoting oxidative stress in the vasculature. Administration of the NOS inhibitorl -NAME to pregnant mice recapitulated the angiotensin sensitivity and oxidative stress observed withsFlt1 overexpression. Sildenafil, an FDA-approved phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor that enhances NO signaling, reversedsFlt1 -induced hypertension and angiotensin II sensitivity in the preeclampsia mouse model. Sildenafil treatment also improved uterine blood flow, decreased uterine vascular resistance, and improved fetal weights in comparison with untreatedsFlt1 -expressing mice. Finally, sFLT1 protein expression inversely correlated with reductions in eNOS phosphorylation in placental tissue of human preeclampsia patients. These data support the concept that endothelial dysfunction due to high circulating sFLT1 may be the primary event leading to enhanced vasoconstrictor sensitivity that is characteristic of preeclampsia and suggest that targeting sFLT1-induced pathways may be an avenue for treating preeclampsia and improving fetal outcomes.Authors
Suzanne D. Burke, Zsuzsanna K. Zsengellér, Eliyahu V. Khankin, Agnes S. Lo, Augustine Rajakumar, Jennifer J. DuPont, Amy McCurley, Mary E. Moss, Dongsheng Zhang, Christopher D. Clark, Alice Wang, Ellen W. Seely, Peter M. Kang, Isaac E. Stillman, Iris Z. Jaffe, S. Ananth Karumanchi
Tomokazu Souma, … , Susan E. Quaggin, Terri L. YoungTomokazu Souma, … , Susan E. Quaggin, Terri L. YoungPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2575-2587. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85830.×Abstract
Primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) is a devastating eye disease and an important cause of childhood blindness worldwide. In PCG, defects in the anterior chamber aqueous humor outflow structures of the eye result in elevated intraocular pressure (IOP); however, the genes and molecular mechanisms involved in the etiology of these defects have not been fully characterized. Previously, we observed PCG-like phenotypes in transgenic mice that lack functional angiopoietin-TEK signaling. Herein, we identified rare
TEK variants in 10 of 189 unrelated PCG families and demonstrated that each mutation results in haploinsufficiency due to protein loss of function. Multiple cellular mechanisms were responsible for the loss of protein function resulting from individual TEK variants, including an absence of normal protein production, protein aggregate formation, enhanced proteasomal degradation, altered subcellular localization, and reduced responsiveness to ligand stimulation. Further, in mice, hemizygosity forTek led to the formation of severely hypomorphic Schlemm’s canal and trabecular meshwork, as well as elevated IOP, demonstrating that anterior chamber vascular development is sensitive toTek gene dosage and the resulting decrease in angiopoietin-TEK signaling. Collectively, these results identifyTEK mutations in patients with PCG that likely underlie disease and are transmitted in an autosomal dominant pattern with variable expressivity.Authors
Tomokazu Souma, Stuart W. Tompson, Benjamin R. Thomson, Owen M. Siggs, Krishnakumar Kizhatil, Shinji Yamaguchi, Liang Feng, Vachiranee Limviphuvadh, Kristina N. Whisenhunt, Sebastian Maurer-Stroh, Tammy L. Yanovitch, Luba Kalaydjieva, Dimitar N. Azmanov, Simone Finzi, Lucia Mauri, Shahrbanou Javadiyan, Emmanuelle Souzeau, Tiger Zhou, Alex W. Hewitt, Bethany Kloss, Kathryn P. Burdon, David A. Mackey, Keri F. Allen, Jonathan B. Ruddle, Sing-Hui Lim, Steve Rozen, Khanh-Nhat Tran-Viet, Xiaorong Liu, Simon John, Janey L. Wiggs, Francesca Pasutto, Jamie E. Craig, Jing Jin, Susan E. Quaggin, Terri L. Young
Carlos A. Ramos, … , Helen E. Heslop, Gianpietro DottiCarlos A. Ramos, … , Helen E. Heslop, Gianpietro DottiPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2588-2596. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86000.×Abstract
BACKGROUND. Treatment of B cell malignancies with adoptive transfer of T cells with a CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) shows remarkable clinical efficacy. However, long-term persistence of T cells targeting CD19, a pan–B cell marker, also depletes normal B cells and causes severe hypogammaglobulinemia. Here, we developed a strategy to target B cell malignancies more selectively by taking advantage of B cell light Ig chain restriction. We generated a CAR that is specific for the κ light chain (κ.CAR) and therefore recognizes κ-restricted cells and spares the normal B cells expressing the nontargeted λ light chain, thus potentially minimizing humoral immunity impairment.METHODS. We conducted a phase 1 clinical trial and treated 16 patients with relapsed or refractory κ+ non-Hodgkin lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (NHL/CLL) or multiple myeloma (MM) with autologous T cells genetically modified to express κ.CAR (κ.CARTs). Other treatments were discontinued in 11 of the 16 patients at least 4 weeks prior to T cell infusion. Six patients without lymphopenia received 12.5 mg/kg cyclophosphamide 4 days before κ.CART infusion (0.2 × 108 to 2 × 108 κ.CARTs/m2). No other lymphodepletion was used.RESULTS. κ.CART expansion peaked 1–2 weeks after infusion, and cells remained detectable for more than 6 weeks. Of 9 patients with relapsed NHL or CLL, 2 entered complete remission after 2 and 3 infusions of κ.CARTs, and 1 had a partial response. Of 7 patients with MM, 4 had stable disease lasting 2–17 months. No toxicities attributable to κ.CARTs were observed.CONCLUSION. κ.CART infusion is feasible and safe and can lead to complete clinical responses.TRIAL REGISTRATION. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00881920.FUNDING. National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants 3P50CA126752 and 5P30CA125123 and Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS) Specialized Centers of Research (SCOR) grant 7018.Authors
Carlos A. Ramos, Barbara Savoldo, Vicky Torrano, Brandon Ballard, Huimin Zhang, Olga Dakhova, Enli Liu, George Carrum, Rammurti T. Kamble, Adrian P. Gee, Zhuyong Mei, Meng-Fen Wu, Hao Liu, Bambi Grilley, Cliona M. Rooney, Malcolm K. Brenner, Helen E. Heslop, Gianpietro Dotti
Martina Absinta, … , Irene C.M. Cortese, Daniel S. ReichMartina Absinta, … , Irene C.M. Cortese, Daniel S. ReichPublished June 6, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2597-2609. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86198.×Abstract
BACKGROUND. In some active multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions, a strong immune reaction at the lesion edge may contain growth and thereby isolate the lesion from the surrounding parenchyma. Our previous studies suggest that this process involves opening of the blood-brain barrier in capillaries at the lesion edge, seen on MRI as centripetal contrast enhancement and a colocalized phase rim. We hypothesized that using these features to characterize early lesion evolution will allow in vivo tracking of tissue degeneration and/or repair, thus improving the evaluation of potential therapies for chronic active lesions.METHODS. Centripetally and centrifugally enhancing lesions were studied in 17 patients with MS using 7-tesla MRI. High-resolution, susceptibility-weighted, T1-weighted (before/after gadolinium), and dynamic contrast–enhanced scans were acquired at baseline and months 1, 3, 6, and 12. For each lesion, time evolution of the phase rim, lesion volume, and T1 hypointensity were assessed. In autopsies of 3 progressive MS cases, the histopathology of the phase rim was determined.RESULTS. In centripetal lesions, a phase rim colocalized with initial contrast enhancement. In 12 of 22, this phase rim persisted after enhancement resolved. Compared with centripetal lesions with transient rim, those with persistent rim had less volume shrinkage and became more T1 hypointense between months 3 and 12. No centrifugal lesions developed phase rims at any time point. Pathologically, persistent rims corresponded to an iron-laden inflammatory myeloid cell population at the edge of chronic demyelinated lesions.CONCLUSION. In early lesion evolution, a persistent phase rim in lesions that shrink least and become more T1 hypointense over time suggests that the rim might mark failure of early lesion repair and/or irreversible tissue damage. In later stages of MS, phase rim lesions continue to smolder, exerting detrimental effects on affected brain tissue.TRIAL REGISTRATION. NCT00001248.FUNDING. The Intramural Research Program of NINDS supported this study.Authors
Martina Absinta, Pascal Sati, Matthew Schindler, Emily C. Leibovitch, Joan Ohayon, Tianxia Wu, Alessandro Meani, Massimo Filippi, Steven Jacobson, Irene C.M. Cortese, Daniel S. Reich
Kipp Weiskopf, … , Irving L. Weissman, Julien SageKipp Weiskopf, … , Irving L. Weissman, Julien SagePublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2610-2620. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81603.×Abstract
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive subtype of lung cancer with limited treatment options. CD47 is a cell-surface molecule that promotes immune evasion by engaging signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα), which serves as an inhibitory receptor on macrophages. Here, we found that CD47 is highly expressed on the surface of human SCLC cells; therefore, we investigated CD47-blocking immunotherapies as a potential approach for SCLC treatment. Disruption of the interaction of CD47 with SIRPα using anti-CD47 antibodies induced macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of human SCLC patient cells in culture. In a murine model, administration of CD47-blocking antibodies or targeted inactivation of the
Cd47 gene markedly inhibited SCLC tumor growth. Furthermore, using comprehensive antibody arrays, we identified several possible therapeutic targets on the surface of SCLC cells. Antibodies to these targets, including CD56/neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), promoted phagocytosis in human SCLC cell lines that was enhanced when combined with CD47-blocking therapies. In light of recent clinical trials for CD47-blocking therapies in cancer treatment, these findings identify disruption of the CD47/SIRPα axis as a potential immunotherapeutic strategy for SCLC. This approach could enable personalized immunotherapeutic regimens in patients with SCLC and other cancers.Authors
Kipp Weiskopf, Nadine S. Jahchan, Peter J. Schnorr, Sandra Cristea, Aaron M. Ring, Roy L. Maute, Anne K. Volkmer, Jens-Peter Volkmer, Jie Liu, Jing Shan Lim, Dian Yang, Garrett Seitz, Thuyen Nguyen, Di Wu, Kevin Jude, Heather Guerston, Amira Barkal, Francesca Trapani, Julie George, John T. Poirier, Eric E. Gardner, Linde A. Miles, Elisa de Stanchina, Shane M. Lofgren, Hannes Vogel, Monte M. Winslow, Caroline Dive, Roman K. Thomas, Charles M. Rudin, Matt van de Rijn, Ravindra Majeti, K. Christopher Garcia, Irving L. Weissman, Julien Sage
Joydeep Ghosh, … , Rebecca J. Chan, Reuben KapurJoydeep Ghosh, … , Rebecca J. Chan, Reuben KapurPublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2621-2625. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI84565.×Abstract
Hyperactivation of the mTOR pathway impairs hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) functions and promotes leukemogenesis. mTORC1 and mTORC2 differentially control normal and leukemic stem cell functions. mTORC1 regulates p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) and eukaryotic initiation factor 4E–binding (eIF4E-binding) protein 1 (4E-BP1), and mTORC2 modulates AKT activation. Given the extensive crosstalk that occurs between mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways, we assessed the role of the mTORC1 substrate S6K1 in the regulation of both normal HSC functions and in leukemogenesis driven by the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) fusion oncogene MLL-AF9. We demonstrated that S6K1 deficiency impairs self-renewal of murine HSCs by reducing p21 expression. Loss of S6K1 also improved survival in mice transplanted with MLL-AF9–positive leukemic stem cells by modulating AKT and 4E-BP1 phosphorylation. Taken together, these results suggest that S6K1 acts through multiple targets of the mTOR pathway to promote self-renewal and leukemia progression. Given the recent interest in S6K1 as a potential therapeutic target in cancer, our results further support targeting this molecule as a potential strategy for treatment of myeloid malignancies.
Authors
Joydeep Ghosh, Michihiro Kobayashi, Baskar Ramdas, Anindya Chatterjee, Peilin Ma, Raghuveer Singh Mali, Nadia Carlesso, Yan Liu, David R. Plas, Rebecca J. Chan, Reuben Kapur
Oh-Joon Kwon, … , Michael M. Ittmann, Li XinOh-Joon Kwon, … , Michael M. Ittmann, Li XinPublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2626-2641. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI84637.×Abstract
Although Notch signaling is deregulated in prostate cancer, the role of this pathway in disease development and progression is not fully understood. Here, we analyzed 2 human prostate cancer data sets and found that higher Notch signaling correlates with increased metastatic potential and worse disease survival rates. We used the
Pten -null mouse prostate cancer model to investigate the function of Notch signaling in the initiation and progression of prostate cancer. Disruption of the transcription factor RBPJ inPten -null mice revealed that endogenous canonical Notch signaling is not required for disease initiation and progression. However, augmentation of Notch activity in this model promoted both proliferation and apoptosis of prostate epithelial cells, which collectively reduced the primary tumor burden. The increase in cellular apoptosis was linked to DNA damage–induced p53 activation. Despite a reduced primary tumor burden, Notch activation inPten -null mice promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition and FOXC2-dependent tumor metastases but did not confer resistance to androgen deprivation. Notch activation also resulted in transformation of seminal vesicle epithelial cells inPten -null mice. Our study highlights a multifaceted role for Notch signaling in distinct aspects of prostate cancer biology and supports Notch as a potential therapeutic target for metastatic prostate cancer.Authors
Oh-Joon Kwon, Li Zhang, Jianghua Wang, Qingtai Su, Qin Feng, Xiang H.F. Zhang, Sendurai A. Mani, Robia Paulter, Chad J. Creighton, Michael M. Ittmann, Li Xin
Asim Saha, … , Laurence A. Turka, Bruce R. BlazarAsim Saha, … , Laurence A. Turka, Bruce R. BlazarPublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2642-2660. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85796.×Abstract
Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) interaction with PD-1 induces T cell exhaustion and is a therapeutic target to enhance immune responses against cancer and chronic infections. In murine bone marrow transplant models, PD-L1 expression on host target tissues reduces the incidence of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). PD-L1 is also expressed on T cells; however, it is unclear whether PD-L1 on this population influences immune function. Here, we examined the effects of PD-L1 modulation of T cell function in GVHD. In patients with severe GVHD, PD-L1 expression was increased on donor T cells. Compared with mice that received WT T cells, GVHD was reduced in animals that received T cells from
Pdl1–/– donors. PD-L1–deficient T cells had reduced expression of gut homing receptors, diminished production of inflammatory cytokines, and enhanced rates of apoptosis. Moreover, multiple bioenergetic pathways, including aerobic glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, and fatty acid metabolism, were also reduced in T cells lacking PD-L1. Finally, the reduction of acute GVHD lethality in mice that receivedPdl1–/– donor cells did not affect graft-versus-leukemia responses. These data demonstrate that PD-L1 selectively enhances T cell–mediated immune responses, suggesting a context-dependent function of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis, and suggest selective inhibition of PD-L1 on donor T cells as a potential strategy to prevent or ameliorate GVHD.Authors
Asim Saha, Roddy S. O’Connor, Govindarajan Thangavelu, Scott B. Lovitch, Durga Bhavani Dandamudi, Caleph B. Wilson, Benjamin G. Vincent, Victor Tkachev, Jan M. Pawlicki, Scott N. Furlan, Leslie S. Kean, Kazutoshi Aoyama, Patricia A. Taylor, Angela Panoskaltsis-Mortari, Rocio Foncea, Parvathi Ranganathan, Steven M. Devine, Joel S. Burrill, Lili Guo, Catarina Sacristan, Nathaniel W. Snyder, Ian A. Blair, Michael C. Milone, Michael L. Dustin, James L. Riley, David A. Bernlohr, William J. Murphy, Brian T. Fife, David H. Munn, Jeffrey S. Miller, Jonathan S. Serody, Gordon J. Freeman, Arlene H. Sharpe, Laurence A. Turka, Bruce R. Blazar
Mårten C.G. Winge, … , Elizabeth A. Waterman, M. Peter MarinkovichMårten C.G. Winge, … , Elizabeth A. Waterman, M. Peter MarinkovichPublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2661-2677. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85738.×Abstract
Interactions between the epidermis and the immune system govern epidermal tissue homeostasis. These epidermis-immune interactions are altered in the inflammatory disease psoriasis; however, the pathways that underlie this aberrant immune response are not well understood. Here, we determined that Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1) is a key mediator of epidermal dysfunction. RAC1 activation was consistently elevated in psoriatic epidermis and primary psoriatic human keratinocytes (PHKCs) exposed to psoriasis-related stimuli, but not in skin from patients with basal or squamous cell carcinoma. Expression of a constitutively active form of RAC1 (RACV12) in mice resulted in the development of lesions similar to those of human psoriasis that required the presence of an intact immune system. RAC1V12-expressing mice and human psoriatic skin showed similar RAC1-dependent signaling as well as transcriptional overlap of differentially expressed epidermal and immune pathways. Coculture of PHKCs with immunocytes resulted in the upregulation of RAC1-dependent proinflammatory cytokines, an effect that was reproduced by overexpressing RAC1 in normal human keratinocytes. In keratinocytes, modulating RAC1 activity altered differentiation, proliferation, and inflammatory pathways, including STAT3, NFκB, and zinc finger protein 750 (ZNF750). Finally, RAC1 inhibition in xenografts composed of human PHKCs and immunocytes abolished psoriasiform hyperplasia and inflammation in vivo. These studies implicate RAC1 as a potential therapeutic target for psoriasis and as a key orchestrator of pathologic epidermis-immune interactions.
Authors
Mårten C.G. Winge, Bungo Ohyama, Clara N. Dey, Lisa M. Boxer, Wei Li, Nazanin Ehsani-Chimeh, Allison K. Truong, Diane Wu, April W. Armstrong, Teruhiko Makino, Matthew Davidson, Daniela Starcevic, Andreas Kislat, Ngon T. Nguyen, Takashi Hashimoto, Bernard Homey, Paul A. Khavari, Maria Bradley, Elizabeth A. Waterman, M. Peter Marinkovich
Yang Xu, … , Joel R. Neilson, Gianpietro DottiYang Xu, … , Joel R. Neilson, Gianpietro DottiPublished June 13, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2678-2688. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85834.×Abstract
Hypoxia occurs in many pathological conditions, including chronic inflammation and tumors, and is considered to be an inhibitor of T cell function. However, robust T cell responses occur at many hypoxic inflammatory sites, suggesting that functions of some subsets are stimulated under low oxygen conditions. Here, we investigated how hypoxic conditions influence human T cell functions and found that, in contrast to naive and central memory T cells (TN and TCM), hypoxia enhances the proliferation, viability, and cytotoxic action of effector memory T cells (TEM). Enhanced TEM expansion in hypoxia corresponded to high hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) expression and glycolytic activity compared with that observed in TN and TCM. We determined that the glycolytic enzyme GAPDH negatively regulates
HIF1A expression by binding to adenylate-uridylate–rich elements in the 3′-UTR region ofHIF1A mRNA in glycolytically inactive TN and TCM. Conversely, active glycolysis with decreased GAPDH availability in TEM resulted in elevated HIF1α expression. Furthermore, GAPDH overexpression reduced HIF1α expression and impaired proliferation and survival of T cells in hypoxia, indicating that high glycolytic metabolism drives increases in HIF1α to enhance TEM function during hypoxia. This work demonstrates that glycolytic metabolism regulates the translation ofHIF1A to determine T cell responses to hypoxia and implicates GAPDH as a potential mechanism for controlling T cell function in peripheral tissue.Authors
Yang Xu, Arindam Chaudhury, Ming Zhang, Barbara Savoldo, Leonid S. Metelitsa, John Rodgers, Jason T. Yustein, Joel R. Neilson, Gianpietro Dotti
Hirokazu Kimura, … , Eiichi Morii, Akira KikuchiHirokazu Kimura, … , Eiichi Morii, Akira KikuchiPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2689-2705. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI84658.×Abstract
Dickkopf1 (DKK1) is a secretory protein that antagonizes oncogenic Wnt signaling by binding to the Wnt coreceptor low-density lipoprotein receptor–related protein 6 (LRP6). DKK1 may also regulate its own signaling to promote cancer cell proliferation, but the mechanism is not understood. Here, we identified cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) as a DKK1 receptor and evaluated CKAP4-mediated DKK1 signaling in cancer cell proliferation. We determined that DKK1 binds CKAP4 and LRP6 with similar affinity but interacts with these 2 receptors with different cysteine-rich domains. DKK1 induced internalization of CKAP4 in a clathrin-dependent manner, further supporting CKAP4 as a receptor for DKK1. DKK1/CKAP4 signaling activated AKT by forming a complex between the proline-rich domain of CKAP4 and the Src homology 3 domain of PI3K, resulting in proliferation of normal cells and cancer cells. Expression of DKK1 and CKAP4 was frequent in tumor lesions of human pancreatic and lung cancers, and simultaneous expression of both proteins in patient tumors was negatively correlated with prognosis and relapse-free survival. An anti-CKAP4 antibody blocked the binding of DKK1 to CKAP4, suppressed AKT activity in a human cancer cell line, and attenuated xenograft tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Together, our results suggest that CKAP4 is a potential therapeutic target for cancers that express both DKK1 and CKAP4.
Authors
Hirokazu Kimura, Katsumi Fumoto, Kensaku Shojima, Satoshi Nojima, Yoshihito Osugi, Hideo Tomihara, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Yasushi Shintani, Hiroko Endo, Masahiro Inoue, Yuichiro Doki, Meinoshin Okumura, Eiichi Morii, Akira Kikuchi
Vanessa Schmidt, … , Gunilla Olivecrona, Thomas E. WillnowVanessa Schmidt, … , Gunilla Olivecrona, Thomas E. WillnowPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2706-2720. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI84708.×Abstract
In humans, genetic variation of sortilin-related receptor, L(DLR class) A repeats containing (
SORL1 ), which encodes the intracellular sorting receptor SORLA, is a major genetic risk factor for familial and sporadic forms of Alzheimer’s disease. Recent GWAS analysis has also associatedSORL1 with obesity in humans and in mouse models, suggesting that this receptor may play a role in regulating metabolism. Here, using mouse models with genetic loss or tissue-specific overexpression of SORLA as well as data from obese human subjects, we observed a gene-dosage effect that links SORLA expression to obesity and glucose tolerance. Overexpression of human SORLA in murine adipose tissue blocked hydrolysis of triacylglycerides and caused excessive adiposity. In contrast,Sorl1 gene inactivation in mice accelerated breakdown of triacylglycerides in adipocytes and protected animals from diet-induced obesity. We then identified the underlying molecular mechanism whereby SORLA promotes insulin-induced suppression of lipolysis in adipocytes. Specifically, we determined that SORLA acts as a sorting factor for the insulin receptor (IR) that redirects internalized receptor molecules from endosomes to the plasma membrane, thereby enhancing IR surface expression and strengthening insulin signal reception in target cells. Our findings provide a molecular mechanism for the association ofSORL1 with human obesity and confirm a genetic link between neurodegeneration and metabolism that converges on the receptor SORLA.Authors
Vanessa Schmidt, Nadja Schulz, Xin Yan, Annette Schürmann, Stefan Kempa, Matthias Kern, Matthias Blüher, Matthew N. Poy, Gunilla Olivecrona, Thomas E. Willnow
Josef Lichtmannegger, … , Karl Heinz Weiss, Hans ZischkaJosef Lichtmannegger, … , Karl Heinz Weiss, Hans ZischkaPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2721-2735. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85226.×Abstract
In Wilson disease (WD), functional loss of ATPase copper-transporting β (ATP7B) impairs biliary copper excretion, leading to excessive copper accumulation in the liver and fulminant hepatitis. Current US Food and Drug Administration– and European Medicines Agency–approved pharmacological treatments usually fail to restore copper homeostasis in patients with WD who have progressed to acute liver failure, leaving liver transplantation as the only viable treatment option. Here, we investigated the therapeutic utility of methanobactin (MB), a peptide produced by
Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b, which has an exceptionally high affinity for copper. We demonstrated that ATP7B-deficient rats recapitulate WD-associated phenotypes, including hepatic copper accumulation, liver damage, and mitochondrial impairment. Short-term treatment of these rats with MB efficiently reversed mitochondrial impairment and liver damage in the acute stages of liver copper accumulation compared with that seen in untreated ATP7B-deficient rats. This beneficial effect was associated with depletion of copper from hepatocyte mitochondria. Moreover, MB treatment prevented hepatocyte death, subsequent liver failure, and death in the rodent model. These results suggest that MB has potential as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of acute WD.Authors
Josef Lichtmannegger, Christin Leitzinger, Ralf Wimmer, Sabine Schmitt, Sabine Schulz, Yaschar Kabiri, Carola Eberhagen, Tamara Rieder, Dirk Janik, Frauke Neff, Beate K. Straub, Peter Schirmacher, Alan A. DiSpirito, Nathan Bandow, Bipin S. Baral, Andrew Flatley, Elisabeth Kremmer, Gerald Denk, Florian P. Reiter, Simon Hohenester, Friedericke Eckardt-Schupp, Norbert A. Dencher, Jerzy Adamski, Vanessa Sauer, Christoph Niemietz, Hartmut H.J. Schmidt, Uta Merle, Daniel Nils Gotthardt, Guido Kroemer, Karl Heinz Weiss, Hans Zischka
Yuk Man Lei, … , Caroline Bartman, Maria-Luisa AlegreYuk Man Lei, … , Caroline Bartman, Maria-Luisa AlegrePublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2736-2744. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85295.×Abstract
Transplantation is the only cure for end-stage organ failure, but without immunosuppression, T cells rapidly reject allografts. While genetic disparities between donor and recipient are major determinants of the kinetics of transplant rejection, little is known about the contribution of environmental factors. Because colonized organs have worse transplant outcome than sterile organs, we tested the influence of host and donor microbiota on skin transplant rejection. Compared with untreated conventional mice, pretreatment of donors and recipients with broad-spectrum antibiotics (Abx) or use of germ-free (GF) donors and recipients resulted in prolonged survival of minor antigen–mismatched skin grafts. Increased graft survival correlated with reduced type I IFN signaling in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and decreased priming of alloreactive T cells. Colonization of GF mice with fecal material from untreated conventional mice, but not from Abx-pretreated mice, enhanced the ability of APCs to prime alloreactive T cells and accelerated graft rejection, suggesting that alloimmunity is modulated by the composition of microbiota rather than the quantity of bacteria. Abx pretreatment of conventional mice also delayed rejection of major antigen–mismatched skin and MHC class II–mismatched cardiac allografts. This study demonstrates that Abx pretreatment prolongs graft survival, suggesting that targeting microbial constituents is a potential therapeutic strategy for enhancing graft acceptance.
Authors
Yuk Man Lei, Luqiu Chen, Ying Wang, Andrew T. Stefka, Luciana L. Molinero, Betty Theriault, Keston Aquino-Michaels, Ayelet S. Sivan, Cathryn R. Nagler, Thomas F. Gajewski, Anita S. Chong, Caroline Bartman, Maria-Luisa Alegre
Souheil-Antoine Younes, … , Scott F. Sieg, Michael M. LedermanSouheil-Antoine Younes, … , Scott F. Sieg, Michael M. LedermanPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2745-2756. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85996.×Abstract
In HIV-1–infected patients, increased numbers of circulating CD8+ T cells are linked to increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Here, we identified a bystander mechanism that promotes CD8 T cell activation and expansion in untreated HIV-1–infected patients. Compared with healthy controls, untreated HIV-1–infected patients have an increased population of proliferating, granzyme B+, CD8+ T cells in circulation. Vβ expression and deep sequencing of CDR3 revealed that in untreated HIV-1 infection, cycling memory CD8 T cells possess a broad T cell repertoire that reflects the repertoire of the resting population. This suggests that cycling is driven by bystander activation, rather than specific antigen exposure. Treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells with IL-15 induced a cycling, granzyme B+ phenotype in CD8+ T cells. Moreover, elevated IL-15 expression in the lymph nodes of untreated HIV-1–infected patients correlated with circulating CD8+ T cell counts and was normalized in these patients following antiretroviral therapy. Together, these results suggest that IL-15 drives bystander activation of CD8+ T cells, which predicts disease progression in untreated HIV-1–infected patients and suggests that elevated IL-15 may also drive CD8+ T cell expansion that is linked to increased morbidity and mortality in treated patients.
Authors
Souheil-Antoine Younes, Michael L. Freeman, Joseph C. Mudd, Carey L. Shive, Arnold Reynaldi, Soumya Panigrahi, Jacob D. Estes, Claire Deleage, Carissa Lucero, Jodi Anderson, Timothy W. Schacker, Miles P. Davenport, Joseph M. McCune, Peter W. Hunt, Sulggi A. Lee, Sergio Serrano-Villar, Robert L. Debernardo, Jeffrey M. Jacobson, David H. Canaday, Rafick-Pierre Sekaly, Benigno Rodriguez, Scott F. Sieg, Michael M. Lederman
Qi Xie, … , Shideng Bao, Jeremy N. RichQi Xie, … , Shideng Bao, Jeremy N. RichPublished June 20, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2757-2772. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI86114.×Abstract
Glioblastomas co-opt stem cell regulatory pathways to maintain brain tumor–initiating cells (BTICs), also known as cancer stem cells. NOTCH signaling has been a molecular target in BTICs, but NOTCH antagonists have demonstrated limited efficacy in clinical trials. Recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (RBPJ) is considered a central transcriptional mediator of NOTCH activity. Here, we report that pharmacologic NOTCH inhibitors were less effective than targeting RBPJ in suppressing tumor growth. While NOTCH inhibitors decreased canonical NOTCH gene expression, RBPJ regulated a distinct profile of genes critical to BTIC stemness and cell cycle progression. RBPJ was preferentially expressed by BTICs and required for BTIC self-renewal and tumor growth. MYC, a key BTIC regulator, bound the
RBPJ promoter and treatment with a bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family bromodomain inhibitor decreased MYC and RBPJ expression. Proteomic studies demonstrated that RBPJ binds CDK9, a component of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), to target gene promoters, enhancing transcriptional elongation. Collectively, RBPJ links MYC and transcriptional control through CDK9, providing potential nodes of fragility for therapeutic intervention, potentially distinct from NOTCH.Authors
Qi Xie, Qiulian Wu, Leo Kim, Tyler E. Miller, Brian B. Liau, Stephen C. Mack, Kailin Yang, Daniel C. Factor, Xiaoguang Fang, Zhi Huang, Wenchao Zhou, Kareem Alazem, Xiuxing Wang, Bradley E. Bernstein, Shideng Bao, Jeremy N. Rich
-
Expression of concern
Sergio Gonzalez, … , Guy Lenaers, Nicolas TricaudSergio Gonzalez, … , Guy Lenaers, Nicolas TricaudPublished April 25, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2773-2773. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88179.×Abstract
Authors
Sergio Gonzalez, Jade Berthelot, Jennifer Jiner, Claire Perrin-Tricaud, Ruani Fernando, Roman Chrast, Guy Lenaers, Nicolas Tricaud
-
Corrigenda
Brian A. Kidd, … , Eric E. Schadt, Joel T. DudleyBrian A. Kidd, … , Eric E. Schadt, Joel T. DudleyPublished July 1, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2773-2773. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88464.×Abstract
Authors
Brian A. Kidd, Gabriel Hoffman, Noah Zimmerman, Li Li, Joseph W. Morgan, Patricia K. Glowe, Gregory J. Botwin, Samir Parekh, Nikolina Babic, Matthew W. Doust, Gregory B. Stock, Eric E. Schadt, Joel T. Dudley
A. Jesse Gore, … , Kelly E. Craven, Murray KorcA. Jesse Gore, … , Kelly E. Craven, Murray KorcPublished July 1, 2016
Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2016;126(7):2774-2774. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88840.×Abstract
Authors
A. Jesse Gore, Samantha L. Deitz, Lakshmi Reddy Palam, Kelly E. Craven, Murray Korc



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)