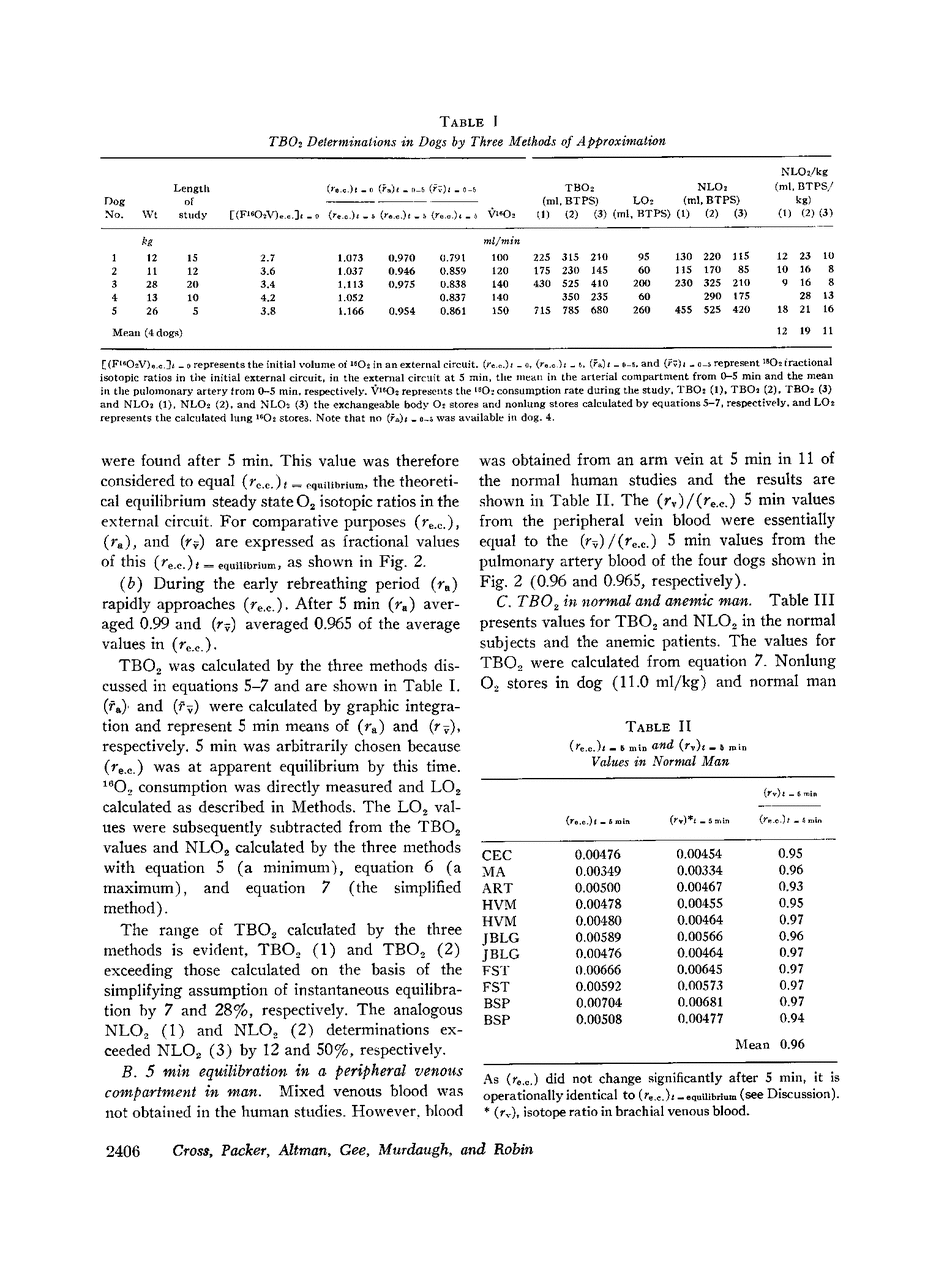
Abstract
A method is described for the measurement of total body exchangeable oxygen stores (TBO2). It is based on the dilution of the stable oxygen isotope, 18O2, by the body exchangeable oxygen stores under circumstances in which 18O2 steady-state equilibrium was evaluated simultaneously for both arterial and venous blood compartments. After evaluation of several simplifying assumptions, TBO2 values in dog, normal man, and anemic patients were measured. The magnitude of the exchangeable nonlung oxygen stores was 11.0 ± 3.1 ml/kg (SD) in 5 dogs, 11.9 ± 2.1 ml/kg in 10 normal subjects, and 7.0 ± 1.6 ml/kg in 8 patients with severe anemia (hematocrits of 25% or less).
Authors
Carroll E. Cross, Bernard S. Packer, Michael Altman, J. Bernard L. Gee, H. Victor Murdaugh Jr., Eugene D. Robin
Other pages:
| 2402 | 2403 | 2404 | 2405 | 2406 | 2407 | 2408 | 2409 | 2410 |