Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2019;129(10):4151-4164. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI127590.
Abstract
While a high frequency of Th1 cells in tumors is associated with improved cancer prognosis, this benefit has been attributed mainly to support of cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells. By attempting to potentiate antibody-driven immunity, we found a remarkable synergy between CD4+ T cells and tumor-binding antibodies. This surprising synergy was mediated by a small subset of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T cells that express the high-affinity Fcγ receptor for IgG (FcγRI) in both mouse and human patients. These cells efficiently lyse tumor cells coated with antibodies through concomitant crosslinking of their T cell receptor (TCR) and FcγRI. By expressing FcγRI and its signaling chain in conventional CD4+ T cells, we successfully employed this mechanism to treat established solid cancers. Overall, this discovery sheds new light on the biology of this T cell subset, their function during tumor immunity, and the means to utilize their unique killing signals in immunotherapy.
Authors
Diana Rasoulouniriana, Nadine Santana-Magal, Amit Gutwillig, Leen Farhat-Younis, Yariv Wine, Corey Saperia, Lior Tal, Haim Gutman, Alexander Tsivian, Ronen Brenner, Eiman Abu Bandora, Nathan E. Reticker-Flynn, Peleg Rider, Yaron Carmi
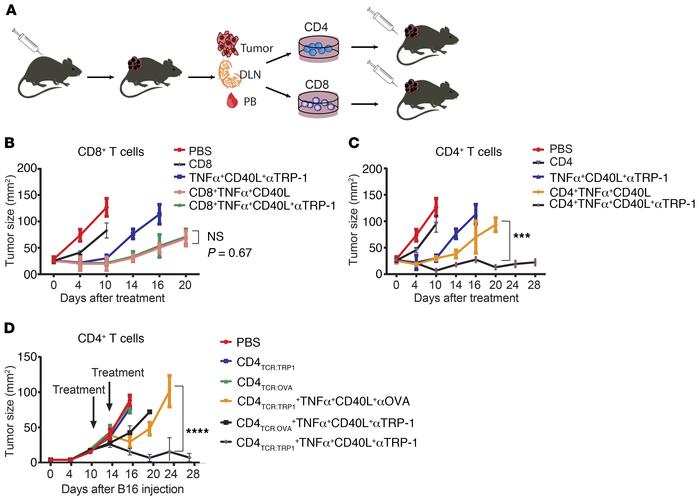
Figure 1
Adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cells with tumor-binding antibodies induces direct killing of tumor cells.



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)