Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2612-2625. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI92233.
Abstract
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is an autosomal dominant human disorder characterized by abnormal bone development that is mainly due to defective intramembranous bone formation by osteoblasts. Here, we describe a mouse strain lacking the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF146 that shows phenotypic similarities to CCD. Loss of RNF146 stabilized its substrate AXIN1, leading to impairment of WNT3a-induced β-catenin activation and reduced Fgf18 expression in osteoblasts. We show that FGF18 induces transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) expression, which is required for osteoblast proliferation and differentiation through transcriptional enhancer associate domain (TEAD) and runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) transcription factors, respectively. Finally, we demonstrate that adipogenesis is enhanced in Rnf146–/– mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Moreover, mice with loss of RNF146 within the osteoblast lineage had increased fat stores and were glucose intolerant with severe osteopenia because of defective osteoblastogenesis and subsequent impaired osteocalcin production. These findings indicate that RNF146 is required to coordinate β-catenin signaling within the osteoblast lineage during embryonic and postnatal bone development.
Authors
Yoshinori Matsumoto, Jose La Rose, Melissa Lim, Hibret A. Adissu, Napoleon Law, Xiaohong Mao, Feng Cong, Paula Mera, Gerard Karsenty, David Goltzman, Adele Changoor, Lucia Zhang, Megan Stajkowski, Marc D. Grynpas, Carsten Bergmann, Robert Rottapel
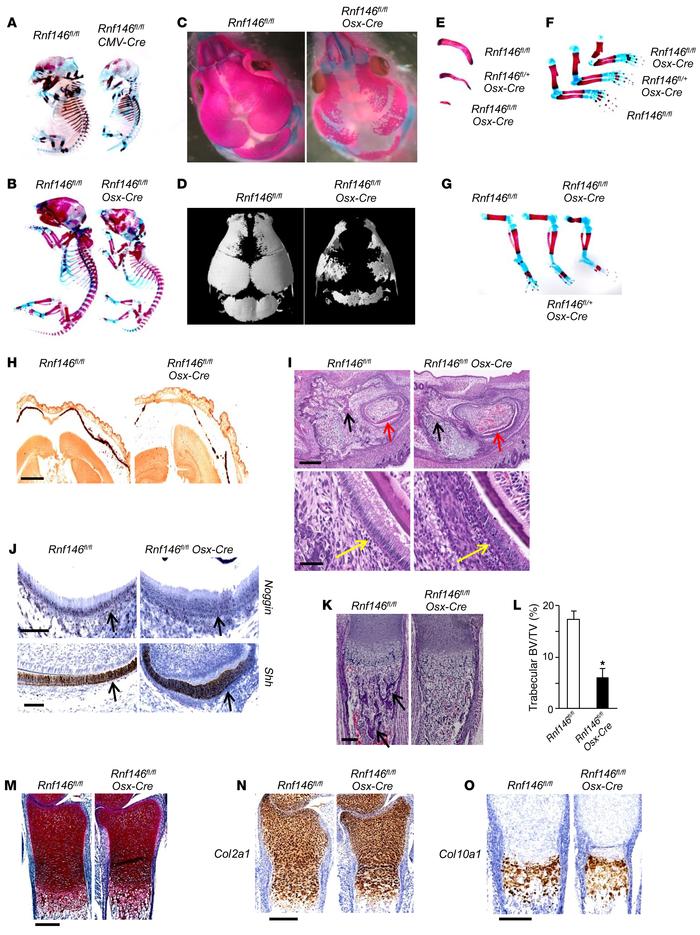
Figure 1
RNF146 deficiency in osteoblasts causes a CCD-like syndrome in mice.



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)