Abstract
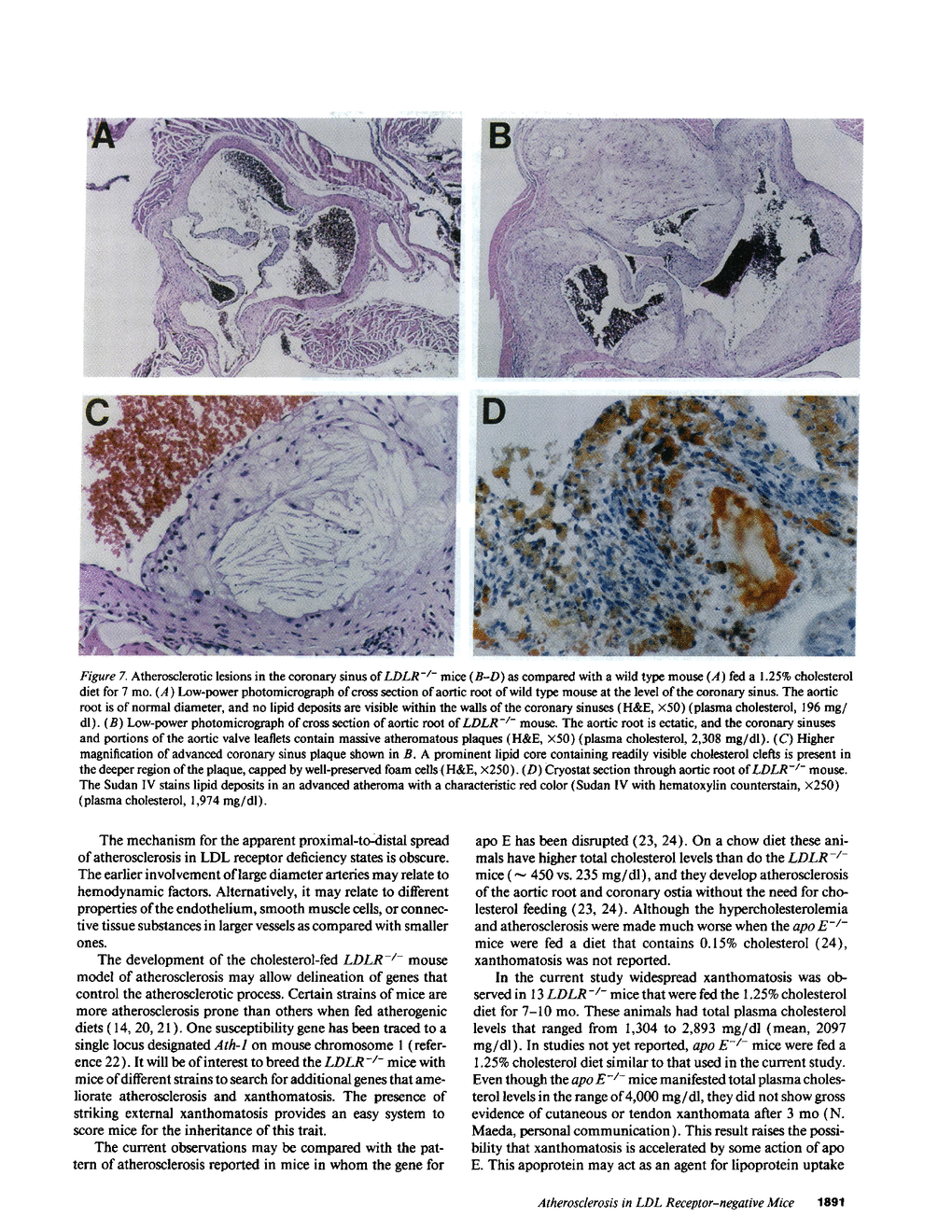
Mice that are homozygous for a targeted disruption of the LDL receptor gene (LDLR-/- mice) were fed a diet that contained 1.25% cholesterol, 7.5% cocoa butter, 7.5% casein, and 0.5% cholic acid. The total plasma cholesterol rose from 246 to > 1,500 mg/dl, associated with a marked increase in VLDL, intermediate density lipoproteins (IDL), and LDL cholesterol, and a decrease in HDL cholesterol. In wild type littermates fed the same diet, the total plasma cholesterol remained < 160 mg/dl. After 7 mo, the LDLR-/- mice developed massive xanthomatous infiltration of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The aorta and coronary ostia exhibited gross atheromata, and the aortic valve leaflets were thickened by cholesterol-laden macrophages. No such changes were seen in the LDLR-/- mice on a normal chow diet, nor in wild type mice that were fed either a chow diet or the high-fat diet. We conclude that LDL receptors are largely responsible for the resistance of wild type mice to atherosclerosis. The cholesterol-fed LDLR-/- mice offer a new model for the study of environmental and genetic factors that modify the processes of atherosclerosis and xanthomatosis.
Authors
S Ishibashi, J L Goldstein, M S Brown, J Herz, D K Burns
Other pages:
| 1885 | 1886 | 1887 | 1888 | 1889 | 1890 | 1891 | 1892 | 1893 |