Abstract
Human airway smooth muscle possesses an inhibitory nonadrenergic noncholinergic neural bronchodilator response mediated by nitric oxide (NO). In guinea pig trachea both endogenous NO and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) modulate cholinergic neural contractile responses. To identify whether endogenous NO or VIP can modulate cholinergic contractile responses in human airways in vitro, we studied the effects of specific NO synthase inhibitors and the peptidase alpha-chymotrypsin on contractile responses evoked by electrical field stimulation (EFS) at three airway levels. Endogenous NO, but not VIP, was shown to inhibit cholinergic contractile responses at all airway levels but this inhibition was predominantly in trachea and main bronchus and less marked in segmental and subsegmental bronchi. To elucidate the mechanism of this modulation we then studied the effects of endogenous NO on acetylcholine (ACh) release evoked by EFS from tracheal smooth muscle strips. We confirmed that release was neural in origin, frequency dependent, and that endogenous NO did not affect ACh release. These findings show that endogenous NO, but not VIP, evoked by EFS can inhibit cholinergic neural responses via functional antagonism of ACh at the airway smooth muscle and that the contribution of this modulation is less marked in lower airways.
Authors
J K Ward, M G Belvisi, A J Fox, M Miura, S Tadjkarimi, M H Yacoub, P J Barnes
Other pages:
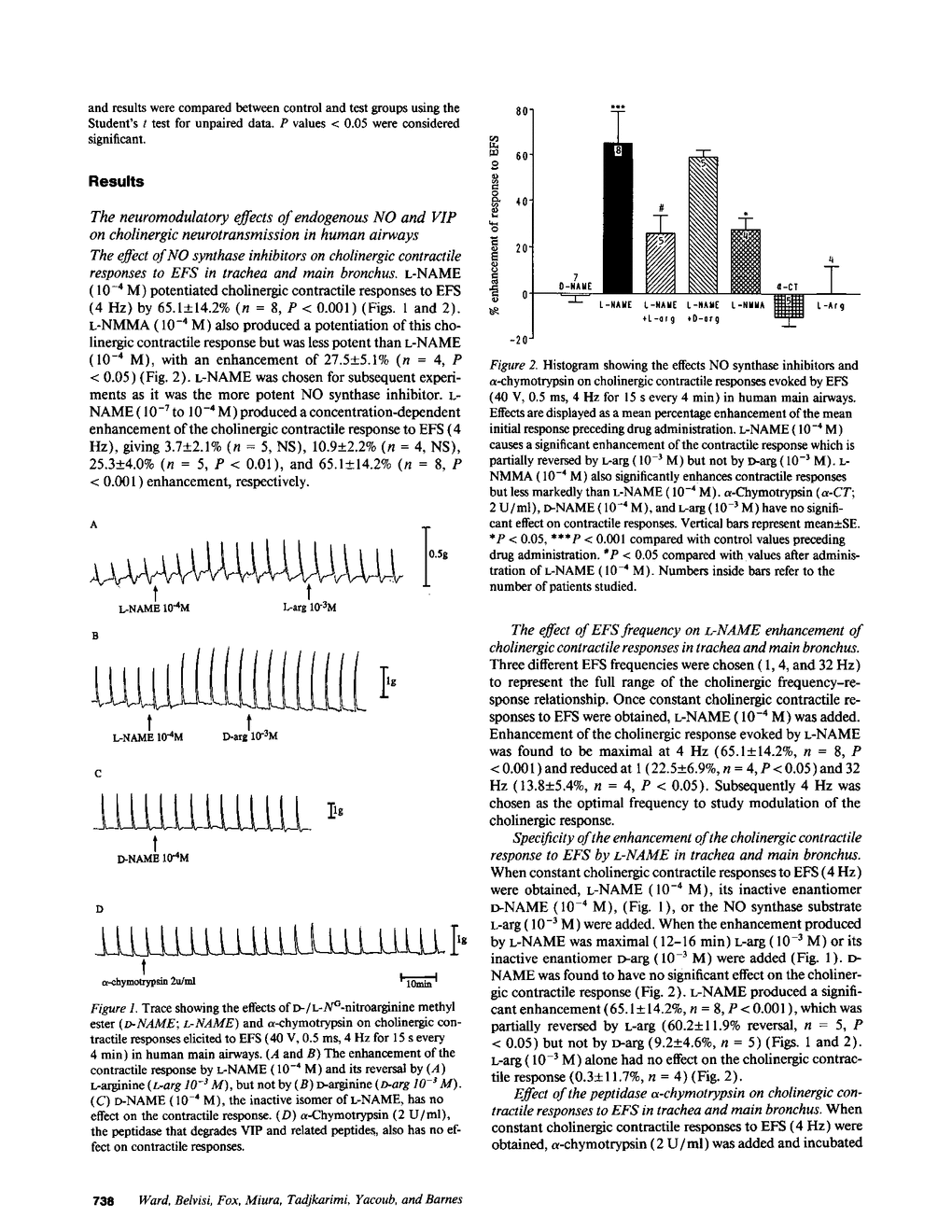
| 736 | 737 | 738 | 739 | 740 | 741 | 742 |