Citation Information: J Clin Invest. 2012;122(10):3439-3447. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI61245.
Abstract
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), a B cell–derived cancer, is one of the most common lymphomas. In HL, the tumor cells — Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells — are usually very rare in the tissue. Although HRS cells are derived from mature B cells, they have largely lost their B cell phenotype and show a very unusual co-expression of markers of various hematopoietic cell types. HRS cells show deregulated activation of multiple signaling pathways and transcription factors. The activation of these pathways and factors is partly mediated through interactions of HRS cells with various other types of cells in the microenvironment, but also through genetic lesions. The transforming events involved in the pathogenesis of HL are only partly understood, but mutations affecting the NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways are frequent. The dependency of HRS cells on microenvironmental interactions and deregulated signaling pathways may offer novel strategies for targeted therapies.
Authors
Ralf Küppers, Andreas Engert, Martin-Leo Hansmann
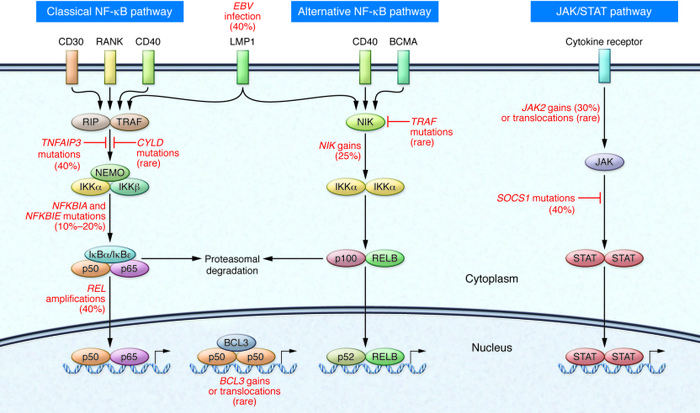
Figure 2
NF-κB and JAK/STAT activity in HRS cells.



Copyright © 2025 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)