Abstract
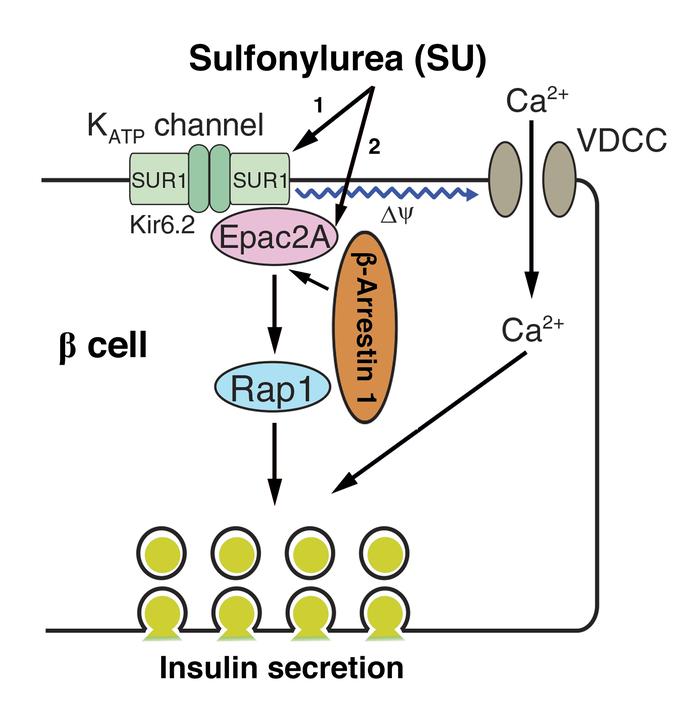
β-Arrestin 1 and 2 (Barr1 and Barr2, respectively) are intracellular signaling molecules that regulate many important metabolic functions. We previously demonstrated that mice lacking Barr2 selectively in pancreatic β cells showed pronounced metabolic impairments. Here we investigated whether Barr1 plays a similar role in regulating β cell function and whole-body glucose homeostasis. Initially, we inactivated the Barr1 gene in β cells of adult mice (β-barr1-KO mice). β-barr1-KO mice did not display any obvious phenotypes in a series of in vivo and in vitro metabolic tests. However, glibenclamide and tolbutamide, 2 widely used antidiabetic drugs of the sulfonylurea (SU) family, showed greatly reduced efficacy in stimulating insulin secretion in the KO mice in vivo and in perifused KO islets in vitro. Additional in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrated that Barr1 enhanced SU-stimulated insulin secretion by promoting SU-mediated activation of Epac2. Pull-down and coimmunoprecipitation experiments showed that Barr1 can directly interact with Epac2 and that SUs such as glibenclamide promote Barr1/Epac2 complex formation, triggering enhanced Rap1 signaling and insulin secretion. These findings suggest that strategies aimed at promoting Barr1 signaling in β cells may prove useful for the development of efficacious antidiabetic drugs.
Authors
Luiz F. Barella, Mario Rossi, Lu Zhu, Yinghong Cui, Fang C. Mei, Xiaodong Cheng, Wei Chen, Vsevolod V. Gurevich, Jürgen Wess
Graphical abstract



Copyright © 2026 American Society for Clinical Investigation
ISSN: 0021-9738 (print), 1558-8238 (online)