Abstract
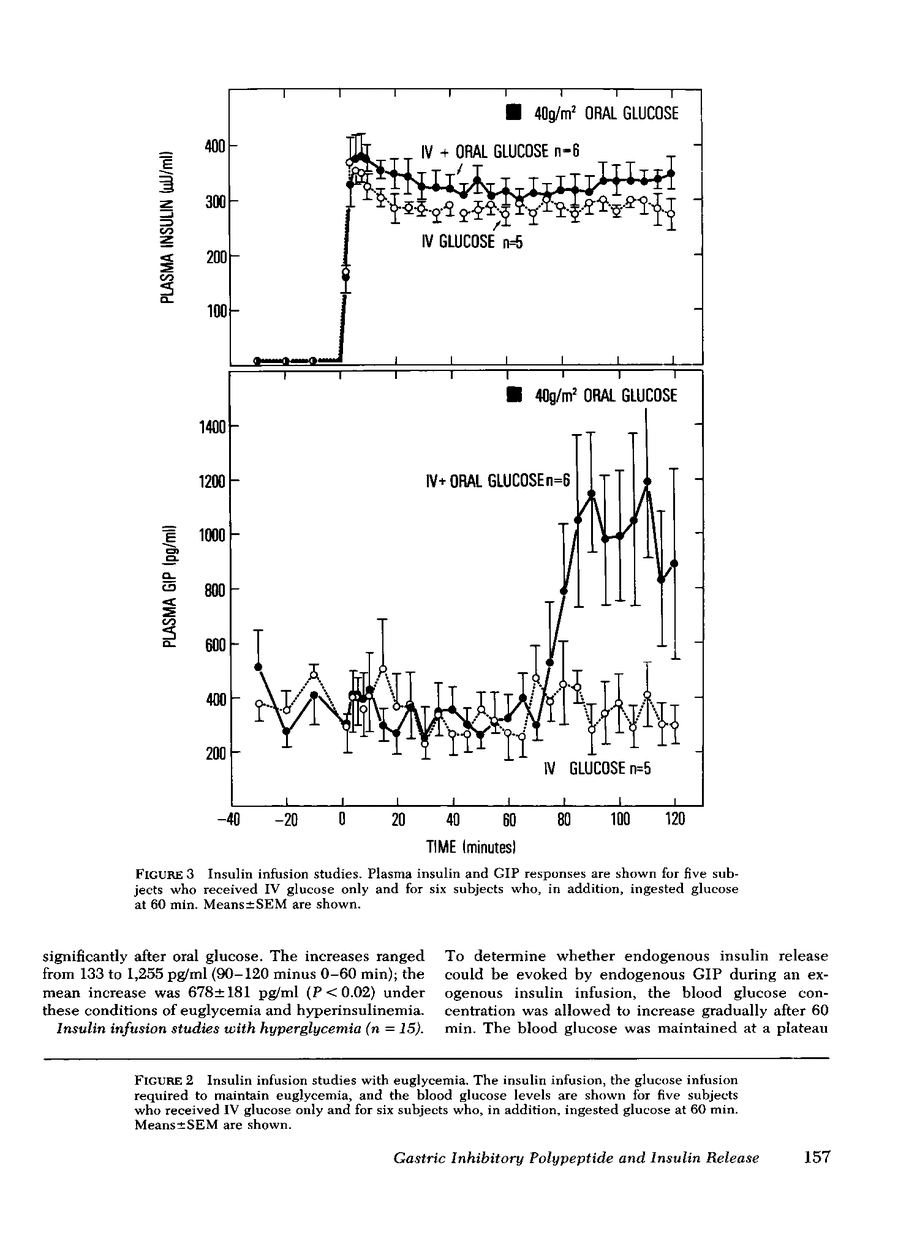
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide, or GIP, has been postulated as the major enteric hormonal mediator of insulin release. The release of immuno-reactive GIP (IR-GIP) after oral glucose and its role in insulin release was studied in normal men by the glucose clamp technique. In 24 subjects studied with the hyperglycemic clamp, blood glucose was maintained at 125 mg/dl above basal for 2 h via a primed-continuous IV glucose infusion coupled to a servo-controlled negative feedback system. 40 g glucose per m2 surface area was ingested at 60 min, and the blood glucose was maintained at the steady-state hyperglycemic level. Plasma IR-GIP and insulin (IRI) levels were measured throughout the 2-h period. IR-GIP levels changed little when IV glucose alone was given; the mean basal value was 305±34 (SEM) pg/ml. After oral glucose, IR-GIP levels began to rise within 10 min and reached a peak within 40 min of 752±105 pg/ml. Plasma IRI responded initially to the square wave of hyperglycemia in the typical biphasic pattern. After oral glucose, plasma IRI levels rose strikingly above the elevated levels produced by hyperglycemia alone, reaching a peak of 170±15 μU/ml within 45 min. The time course of the rise in IR-GIP and IRI was nearly identical.
Authors
Dana K. Andersen, Dariush Elahi, John C. Brown, Jordan D. Tobin, Reubin Andres
Other pages:
| 152 | 153 | 154 | 155 | 156 | 157 | 158 | 159 | 160 | 161 |